Research
COVID-19 Uncertainty and Its Impact on Stock Prices
Independent research paper (Sept. 2021 – June 2022); Forthcoming publication at Journal of Student Research
Abstract :
This paper develops a stock-pricing model to investigate how the COVID-19 induced uncertainty affects stock prices. Through utilizing a series of mathematical techniques and conducting a comparative static analysis, we find that when economic uncertainty intensifies, the future payouts of firms, such as dividend payments to stockholders, tend to diminish, indicating a deterioration of firms’ stability and prospect. As a result, investors expect a reduction in the future payoffs of the stocks issued by firms. Given that the price of a stock reflects the present values of its expected future payoffs, the rising level of COVID-19 uncertainty, which undermines the future payoffs of the stocks that investors expect to receive, decreases stock prices.
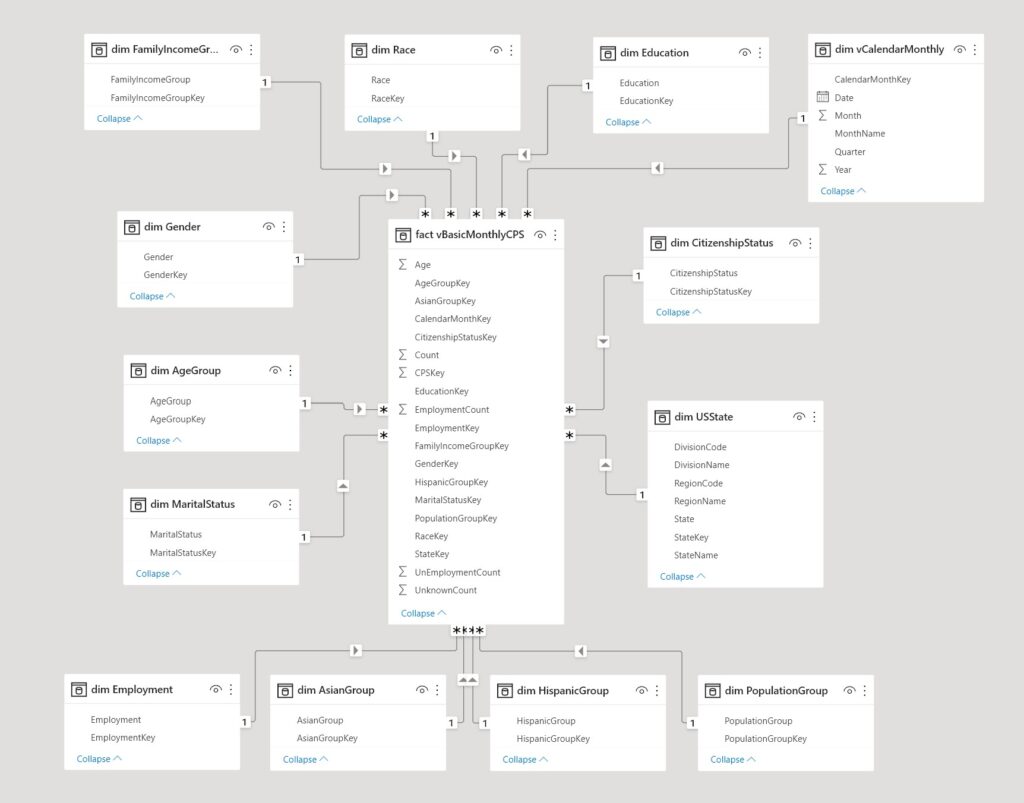
The Unemployment Rates of U.S. Disadvantaged Workers during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Independent research report of data science project (Nov. 2021 – Apr. 2022), presented findings and received 2nd place in Data Science and Analytics at PA TSA competition during April 20-23, 2022.
TSA national competition qualifier.
Financial Development and Policy Effectiveness
Working paper (July 2022 – Present), coauthoring with Prof. Niraj Koirala at California State University,
Abstract:
This paper examines the relationship between financial development, financial openness, and policy effectiveness in stimulating the economy. Using panel data from 98 countries from 1980 to 2018, the paper finds that financial development and financial openness diminish the efficacy of monetary and tax policies on output growth. Furthermore, the paper finds that the dampening effect of financial development on policy effectiveness is larger in the countries with higher level of financial development compared to those with lower level of development. Additionally, the paper also studies the international spillover effects of US economic crises and the role of financial development and policy variables in spurring output growth. Using dynamic panel GMM model, we find that the capacity of monetary policy on increasing output growth decreases during the crises time. However, strong financial institution in a country offsets the negative impacts of the US economic crises partially.
Keywords: Financial Development; Financial Openness; Policy Effectiveness; International Spillover Effects of US Crises
JEL Classiffcation Codes: E52, G21